Reading Notes of How does GPT Obtain its Ability? Tracing Emergent Abilities of Language Models to their Sources
Reading notes of Yao’s notes of How does GPT Obtain its Ability? Tracing Emergent Abilities of Language Models to their Sources (notion.site).
Keywords: code and instruction tuning; trade of between in-context learning and instruction tuning; unlock or inject the abilities; instruction-tuning, supervised instruction-tuning, and RLHF instruction-tuning; knowledge and reasoning.
Reference
Fu, Yao; Peng, Hao and Khot, Tushar. (Dec 2022). How does GPT Obtain its Ability? Tracing Emergent Abilities of Language Models to their Sources. Yao Fu’s Notion. https://yaofu.notion.site/How-does-GPT-Obtain-its-Ability-Tracing-Emergent-Abilities-of-Language-Models-to-their-Sources-b9a57ac0fcf74f30a1ab9e3e36fa1dc1
Road Map
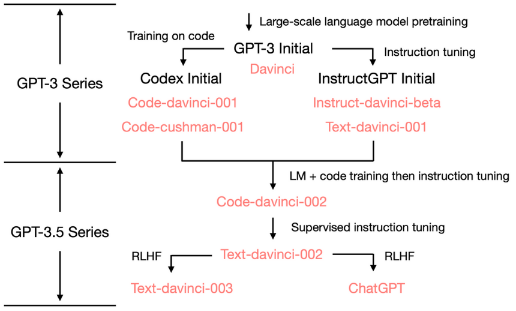
Note: The base model for code-davinci-002 is highly likely not be the initial GPT-3 davinci model.
Summary
The authors’ conclusion:
- The language generation ability + basic world knowledge + in-context learning are from pretraining (
davinci) - The ability to store a large amount of ==knowledge== is from the 175B scale.
- The ability to follow instructions and generalizing to new tasks are from scaling instruction tuning (
davinci-instruct-beta) - The ability to perform complex ==reasoning== is likely to be from training on code (
code-davinci-002) - The ability to generate neutral, objective, safe, and informative answers are from alignment with human. Specifically:
- If supervised tuning, the resulting model is
text-davinci-002 - If RLHF, the resulting model is
text-davinci-003 - Either supervised or RLHF, the models cannot outperform
code-davinci-002on many tasks, which is called the alignment tax. (RLHF on 003 just recovers the in-context learning ability.)
- If supervised tuning, the resulting model is
- The dialog ability is also from RLHF (
ChatGPT), specifically it tradeoffs in-context learning for:- Modeling dialog history
- Increased informativeness
- Rejecting questions outside the model’s knowledge scope
| Ability | OpenAI Model | Training Method | OpenAI API | OpenAI Paper | Open Source Approximate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-3 Series | |||||
| Generation + World Knowledge + In-context Learning |
GPT-3 Initial Many abilities already within this model, although superficially weak |
Language Modeling | Davinci | GPT 3 Paper | Meta OPT BLOOM Galactica |
| + Follow Human Instruction + Generalize to unseen task (free lunch of scaling instructions) |
Instruct-GPT initial | Instruction Tuning | Davinci-Instruct-Beta | Instruct-GPT paper | T0 paper Google FLAN paper Google FLAN paper |
| + Code Understanding + Code Generation |
Codex initial | Training on Code | Code-Cushman-001 | Codex Paper | Salesforce CodeGen |
| GPT-3.5 Series | |||||
| ++ Code Understanding ++ Code Generation ++ Complex Reasoning / Chain of Thought (why?) + Long-term dependency (probably) |
Current Codex Strongest model in GPT3.5 Series |
Training on text + code Tuning on instructions |
Code-Davinci-002 | Codex Paper | ?? |
| ++ Follow Human Instruction - In-context learning - Reasoning ++ Zero-shot generation |
Instruct-GPT supervised Trade in-context learning for zero-shot generation |
Supervised instruction tuning | Text-Davinci-002 | Instruct-GPT paper, supervised part | T0 paper Google FLAN paper Google FLAN paper |
| + Follow human value + More detailed generation + In-context learning + Zero-shot generation |
Instruct-GPT RLHF More aligned than 002, less performance loss |
Instruction tuning w. RLHF | Text-Davinci-003 | Instruct-GPT paper, RLHF part Summarization .w human feedback | DeepMind Sparrow paper AI2 RL4LMs |
| ++ Follow human value ++ More detailed generation ++ Reject questions beyond its knowledge (why?) ++ Model dialog context – In-context learning |
ChatGPT Trade in-context learning for dialog history modeling |
Tuning on dialog w. RLHF | - | - | DeepMind Sparrow paper AI2 RL4LMs |
Limitations
- On-the-fly overwriting the model’s belief: when the model expresses its belief in something, it might be hard to correct it when the belief is wrong. There seems to be a hierarchy of how strong the belief is, which means that there exists a list of very strong core belief. ==It is extremely important to ensure such core belief should be absolutely 100% aligned with human.==
- Formal reasoning: the GPT-3.5 series cannot do reasoning within formal, strict systems like math or first-order logic.
- The word “reasoning” is less well-defined. Yet if we view there is a spectrum of ambiguity like (a) very ambiguous, no reasoning; (b) mixture of logic and ambiguous statements; ©. no ambiguity has to be very rigorous, then,
- The model can do very well on type (b) reasoning with ambiguity.
- The model cannot do type © reasoning, yet whether such reasoning should be done by a language model or a symbolic system is up for discussion.
- Update: Wolfram|Alpha as the Way to Bring Computational Knowledge Superpowers to ChatGPT—Stephen Wolfram Writings
- Retrieval from the Internet: the GPT-3.5 series cannot directly search the internet (for now)
- Likely tested within OpenAI: WebGPT: Improving the Factual Accuracy of Language Models through Web Browsing (openai.com)
- Seperate the knowledge and reasoning: it would be ideal if we could offload the knowledge part to the outside retrieval system and let the language model only focus on reasoning.
- Combining LLMs (reasoning) and search (knowledge) is a good direction: LLMs are good for reasoning, not for knowledge. The knowledge within LLMs are unreliable and cannot be verified. On the other hand, the knowledge from search engine is orders or magnitude larger than LLM’s internal knowledge, can one can easily verify credibility of search results by checking the source.
- Retrieval-augmented models?
- Reduce the model size? (175B storing unreliable knowledge -> search engines)
Questions to be answered
- How does the GPT-3.5 acquire the reasoning ability (CoT)? (Likely because of code training according to the authors).
- Which kinds of abilities are unlocked/injected by what means<span class=“hint–top hint–rounded” aria-label=““by what means” is hypothesized in the summary section but some of them are not proved.”>[1]? The authors’ hypothesis (according to scale):
- Abilities from code training: injection
- Abilities from instruction tuning: unlock
What I need to further know about
- instruction-tuning? supervised instruction-tuning? RLHF instruction-tuning?
- code training?